PyTorch 资料
PyTorch
1.7.0 文档
https://www.w3cschool.cn/pytorch/pytorch-mrni3btn.html
https://handbook.pytorch.wiki/chapter1/1.1-pytorch-introduction.html
LSTM细节分析理解(pytorch版):https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/79064602
OLD:https://www.pytorch123.com/SixthSection/Dcgan/
PyTorch 学习笔记汇总(完结撒花) - 张贤同学的文章 - 知乎
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/265394674
PyTorch 学习笔记
在线电子书:https://pytorch.zhangxiann.com/
配套代码:https://github.com/zhangxiann/PyTorch_Practice
一、基本概念
1.1 Pytorch 简介与安装
1.2 Tensor 张量介绍

1.2.1 直接创建 Tensor
torch.tensor()
1
| torch.tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None, requires_grad=False, pin_memory=False)
|
- data: 数据,可以是 list,numpy
- dtype: 数据类型,默认与 data 的一致
- device: 所在设备,cuda/cpu
- requires_grad: 是否需要梯度
- pin_memory: 是否存于锁页内存
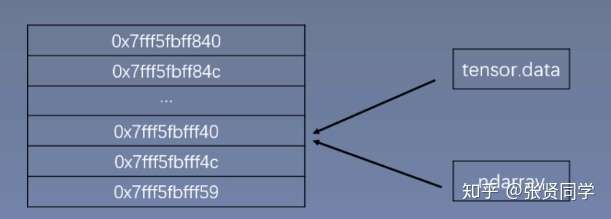
torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
从 numpy 创建 tensor。利用这个方法创建的 tensor 和原来的
ndarray 共享内存,当修改其中一个数据,另外一个也会被改动。
 img
img
1.2.2 根据数值创建 Tensor
torch.zeros():根据 size
创建全 0 张量
1
| torch.zeros(*size, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
- size: 张量的形状
- out: 输出的张量,如果指定了
out,那么
torch.zeros()返回的张量和 out
指向的是同一个地址
- layout: 内存中布局形式,有 strided,sparse_coo
等。当是稀疏矩阵时,设置为 sparse_coo 可以减少内存占用。
- device: 所在设备,cuda/cpu
- requires_grad: 是否需要梯度
torch.full(),torch.full_like():创建自定义数值的张量
1
| torch.full(size, fill_value, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
- size: 张量的形状,如 (3,3)
- fill_value: 张量中每一个元素的值
torch.arange():创建等差的
1 维张量。注意区间为[start, end)。
1
| torch.arange(start=0, end, step=1, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
- start: 数列起始值
- end: 数列结束值,开区间,取不到结束值
- step: 数列公差,默认为 1
torch.linspace():创建均分的
1 维张量。数值区间为 [start, end]
1
| torch.linspace(start, end, steps=100, out=None, dtype=None, layout=torch.strided, device=None, requires_grad=False)
|
- start: 数列起始值
- end: 数列结束值
- steps: 数列长度 (元素个数)
1.2.3 根据概率创建 Tensor
torch.normal()
1
| torch.normal(mean, std, *, generator=None, out=None)
|
功能:生成正态分布 (高斯分布)
==1.3 张量操作与线性回归==
==1.3.1 拼接==:cat、stack
torch.cat():将张量按照
dim 维度进行拼接
1
| torch.cat(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
|
- tensors: 张量序列 [t, t]
- dim: 要拼接的维度
torch.stack():将张量在==新创建的
dim 维度==上进行拼接,已有维度后移
1
| torch.stack(tensors, dim=0, out=None)
|
- tensors: 张量序列
- dim: 要拼接的维度
==1.3.2 切分==:chunk、split
torch.chunk():将张量按照维度
dim 进行平均切分。若不能整除,则最后一份张量小于其他张量。
1
2
| torch.chunk(input, chunks, dim=0)
torch.chunk(a, dim=1, chunks=3)
|
- input: 要切分的张量
- chunks: 要切分的份数
- dim: 要切分的维度
torch.split():将张量按照维度
dim 进行平均切分。可以指定每一个==分量的切分长度==。
1
2
| torch.split(tensor, split_size_or_sections, dim=0)
torch.split(t, [2, 1, 2], dim=1)
|
- tensor: 要切分的张量
- split_size_or_sections: 为 int
时,表示每一份的长度,如果不能被整除,则最后一份张量小于其他张量;为
list 时,按照 list 元素作为每一个分量的长度切分。如果 list
元素之和不等于切分维度 (dim) 的值,就会报错。
- dim: 要切分的维度
==1.3.3 索引==
torch.index_select():在维度
dim 上,按照 index 索引取出数据拼接为张量返回。
1
| torch.index_select(input, dim, index, out=None)
|
功能:在维度 dim 上,按照 index
索引取出数据拼接为张量返回。torch.tensor([0, 2], dtype=torch.long)
- input: 要索引的张量
- dim: 要索引的维度
- index: 要索引数据的序号
torch.mask_select():按照
mask 中的 True 进行索引拼接得到一维张量返回。
1
| torch.masked_select(input, mask, out=None)
|
- 要索引的张量
- mask: 与 input 同形状的布尔类型张量
==1.3.4 变换==
torch.reshape():变换张量的形状。当张量在内存中是连续时,返回的张量和原来的张量共享数据内存,改变一个变量时,另一个变量也会被改变。
1
2
| torch.reshape(input, shape)
torch.reshape(t, (-1, 2, 2))
|
- input: 要变换的张量
- shape: 新张量的形状
torch.transpose():交换张量的两个维度。常用于图像的变换,比如把c*h*w变换为h*w*c。
1
| torch.transpose(input, dim0, dim1)
|
- input: 要交换的变量
- dim0: 要交换的第一个维度
- dim1: 要交换的第二个维度
torch.t():2
维张量转置,对于 2
维矩阵而言,等价于torch.transpose(input, 0, 1)。
torch.squeeze():压缩长度为 1
的维度
1
| torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, out=None)
|
- dim: 若为 None,则移除所有长度为 1
的维度;若指定维度,则当且仅当该维度长度为 1 时可以移除。
torch.unsqueeze():根据
dim 扩展维度,长度为 1。
1
| torch.unsqueeze(input, dim)
|
==1.3.5 张量的数学运算==
加减乘除,对数,指数,幂函数
和三角函数。
torch.add():
逐元素计算 input + alpha *
other。因为在深度学习中经常用到先乘后加的操作。
1
2
| torch.add(input, other, out=None)
torch.add(input, other, *, alpha=1, out=None)
|
- input: 第一个张量
- alpha: 乘项因子
- other: 第二个张量
torch.addcdiv()
1
| torch.addcdiv(input, tensor1, tensor2, *, value=1, out=None)
|
计算公式为:out ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=_%7Bi%7D%3D%5Coperatorname%7Binput%7D_%7Bi%7D%2B) value
value ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%5Ctimes+%5Cfrac%7B%5Ctext+%7B+tensor+%7D+1_%7Bi%7D%7D%7B%5Ctext+%7B+tensor+%7D+2_%7Bi%7D%7D)
torch.addcmul()
1
| torch.addcmul(input, tensor1, tensor2, *, value=1, out=None)
|
计算公式为:out ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=_%7Bi%7D%3D) input
input ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=_%7Bi%7D%2B) value
value ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%5Ctimes) tensor
tensor
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=1_%7Bi%7D+%5Ctimes) tensor
tensor ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=2_%7Bi%7D)
==Pytorch 线性回归==
线性回归是分析一个变量 (![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=y) ) 与另外一
(多) 个变量 (
) 与另外一
(多) 个变量 (![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=x) ) 之间的关系的方法。一般可以写成
) 之间的关系的方法。一般可以写成 ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=y%3Dwx%2Bb) 。线性回归的目的就是求解参数
。线性回归的目的就是求解参数 ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=w%2C+b) 。
。
线性回归的求解可以分为 3 步:
- 确定模型:
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=y%3Dwx%2Bb)
- 选择损失函数,一般使用均方误差 MSE:
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=%5Cfrac%7B1%7D%7Bm%7D+%5Csum_%7Bi%3D1%7D%5E%7Bm%7D%5Cleft%28y_%7Bi%7D-%5Chat%7By%7D_%7Bi%7D%5Cright%29%5E%7B2%7D) 。其中
。其中 ![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=+%5Chat%7By%7D_%7Bi%7D+) 是预测值,
是预测值,![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=y) 是真实值。
是真实值。
- 使用梯度下降法求解梯度 (其中
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=lr) 是学习率),并更新参数:
是学习率),并更新参数:
-
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=w+%3D+w+-+lr+%2A+w.grad) [公式]
[公式]
-
![[公式]](https://www.zhihu.com/equation?tex=b+%3D+b+-+lr+%2A+b.grad) [公式]
[公式]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| 代码如下:
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
torch.manual_seed(10)
lr = 0.05
x = torch.rand(20, 1) * 10
y = 2*x + (5 + torch.randn(20, 1))
w = torch.randn((1), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros((1), requires_grad=True)
for iteration in range(1000):
wx = torch.mul(w, x)
y_pred = torch.add(wx, b)
loss = (0.5 * (y - y_pred) ** 2).mean()
loss.backward()
b.data.sub_(lr * b.grad)
w.data.sub_(lr * w.grad)
w.grad.zero_()
b.grad.zero_()
if iteration % 20 == 0:
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(), y.data.numpy())
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(), y_pred.data.numpy(), 'r-', lw=5)
plt.text(2, 20, 'Loss=%.4f' % loss.data.numpy(), fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
plt.xlim(1.5, 10)
plt.ylim(8, 28)
plt.title("Iteration: {}\nw: {} b: {}".format(iteration, w.data.numpy(), b.data.numpy()))
plt.pause(0.5)
if loss.data.numpy() < 1:
break
|


value
input
value
tensor
tensor
) 与另外一
(多) 个变量 (
) 之间的关系的方法。一般可以写成
。线性回归的目的就是求解参数
。
。其中
是预测值,
是真实值。
是学习率),并更新参数: